This Blog helps you to define your all problems regarding Computer Sc. Info Technology and Management. In this Blog you'll get your topic, solution for your questions as well as you get knowledge about new technologies and Corporate world updates also. Here you'll also get new ideas, techniques, various useful websites links and many more. Please also suggest me, what more i do for this Blog and for its enhancements. WELCOME suggestions & queries at amitesh_km@hotmail.com
Friday, May 28, 2021
Monday, May 10, 2021
Three-Schema Architecture (3 view of DBMS)
Data Abstraction
Data abstraction is hiding the complex data structure in order to simplify the user’s interface of the system. It is done because many of the users interacting with the database system are not that much computer trained to understand the complex data structures of the database system.
To achieve data abstraction, we will discuss a Three-Schema architecture which abstracts the database at three levels discussed below:
Three-Schema Architecture:
The main objective of this architecture is to have an effective separation between the user interface and the physical database. So, the user never has to be concerned regarding the internal storage of the database and it has a simplified interaction with the database system.
The three-schema architecture defines the view of data at three levels:
- Physical level (internal level/view)
- Logical level (conceptual level/view)
- View level (external level/view)
1. Physical Level/ Internal Level
The physical or the internal level schema describes how the data is stored in the hardware. It also describes how the data can be accessed. The physical level shows the data abstraction at the lowest level and it has complex data structures. Only the database administrator operates at this level.
2. Logical Level/ Conceptual Level
It is a level above the physical level. Here, the data is stored in the form of the entity set, entities, their data types, the relationship among the entity sets, user operations performed to retrieve or modify the data and certain constraints on the data. Well adding constraints to the view of data adds the security. As users are restricted to access some particular parts of the database.
It is the developer and database administrator who operates at the logical or the conceptual level.
3. View Level/ User level/ External level
It is the highest level of data abstraction and exhibits only a part of the whole database. It exhibits the data in which the user is interested. The view level can describe many views of the same data. Here, the user retrieves the information using different application from the database.
Schema in DBMS
The term "database schema" can refer to a visual representation of a database, a set of rules that govern a database, or to the entire set of objects belonging to a particular user.
A database schema represents the logical configuration of all or part of a relational database. It can exist both as a visual representation and as a set of formulas known as integrity constraints that govern a database. These formulas are expressed in a data definition language, such as SQL. As part of a data dictionary, a database schema indicates how the entities that make up the database relate to one another, including tables, views, stored procedures, and more.
There are two main kinds of database schema:
- A logical database schema conveys the logical constraints that apply to the stored data. It may define integrity constraints, views, and tables.
- A physical database schema lays out how data is stored physically on a storage system in terms of files and indices.
What is sub schema?
Thursday, April 29, 2021
INTRODUCTION & CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPUTER
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER
Computer is an electronic device which takes input from user, processes it according to instructions and gives the desired output. It is basically a programmable machine. It works on binary digits, in short binary digit is known as bit. Computer was developed to produce accurate result at a very fast speed.
CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPUTERS
1. Speed: A computer is very fast device; it can perform a work in a few second. The amount of work that a human being can do in an entire year, a computer can do in a few minutes or in seconds.
While talking about the speed of a
computer we do not talk in terms of seconds or even milliseconds (![]() but in terms of microseconds (
but in terms of microseconds (![]() ,
nanoseconds (
,
nanoseconds (![]() ,
and even picoseconds (
,
and even picoseconds (![]() .
A powerful computer is capable of performing several billion (
.
A powerful computer is capable of performing several billion (![]() simple arithmetic operations per second.
simple arithmetic operations per second.
2. Power of Remembering: As a human being acquires new knowledge, his/her brain selects what it feels to be important and forgets unimportant things. This is not the case with computers. A computer can store and recall any amount of information because of its secondary storage capacity. It can retain a piece of information as long as a user desires and the user can recall the information whenever required. Even after several years, a user can recall exactly the same information that he/she had stored in the computer several years ago. A computer forgets or looses certain information only when a user asks it to do so. Hence, it is entirely depend upon to the user to make a computer retain or forget some information.
3. Accuracy: It provides a high degree of accuracy. It can accurately gives the result of division of any two numbers up to 10 decimal places.
4. Diligence: Computer, being a machine, does not suffer from the tiredness and lack of concentration. If millions of calculations to be performed then the computer will perform the last calculation with the same accuracy and speed as the first calculation.
5. Intelligence: It has no I.Q. It possesses no intelligence of its own.
Tuesday, March 16, 2021
Plotter
A plotter is a special output device used to produce hard copies of large graphs and designs on paper, such as construction maps, engineering drawings, architectural plans and business charts. The plotter is either a peripheral component that you add to your computer system or a standalone device with its own internal processor.
A plotter is a computer hardware device much like a printer that is used for printing vector graphics. Instead of toner, plotters use a pen, pencil, marker, or another writing tool to draw multiple, continuous lines onto paper rather than a series of dots like a traditional printer. Though once widely used for computer-aided design, these devices have more or less been phased out by wide-format printers.
Advantages of plotters
- Plotters can work on very large sheets of paper while maintaining high resolution.
- They can print on a wide variety of flat materials including plywood, aluminum, sheet steel, cardboard, and plastic.
- Plotters allow the same pattern to be drawn thousands of times without any image degradation.
Disadvantages of plotters
- Plotters are quite large compared to a traditional printer.
- Plotters are also much more expensive than a traditional printer
Tuesday, November 10, 2020
UNIX Commands List
File/Directory operation related Unix Commands
- cp – copy a file
- mv – move or rename files or directories
- tar – create and use archives of files
- gzip – compress a file
- ftp – file transfer program
- lpr – print out a file
- mkdir – make a directory
- rm – remove files or directories
- rmdir – remove a directory
- mount – attaches a file system to the file system hierarchy at the mount_point, which is the pathname of a directory.
- umount – unmounts a currently mounted file system.
Navigational type Unix Commands
- cd – change directory
- pwd – display the name of your current directory
- ls – list names of files in a directory
Disk, File and Folder Size/Usage
- du – Use this command to see the size/usage of the folder you are in. Example usage: du -sk *
- df – Report file system disk space usage. Example usage: df -k
Display file content
- cat – concatenate and display files.
- more – The more utility is a filter that displays the contents of a text file on the terminal, one screenful at a time.
- less – Less is a program similar to more (1), but which allows backward movement in the file as well as forward movement. Also, less does not have to read the entire input file before starting,so with large input files it starts up faster than text editors like vi
File Editing
- vi – The vi (visual) utility is a display-oriented text editor.
- nano – nano is a small, free and friendly editor.
Search
- find – find files of a specified name or type.
- grep – searches files for a specified string or expression.
Administration
- top – Top displays the top 10 processes on the system and periodically updates this information. Raw cpu percentage is used to rank the processes.
- chmod – change the permissions of a file or a directory.
- ps – The ps command prints information about active processes.
- kill – kill a process.
Information
- date – display the current date and time.
- cal – The cal utility writes a Gregorian calendar to standard output.
- diff – display differences between text files.
Help Related
- man – The man command displays information from the reference manuals.
- help – The help utility retrieves information to further explain errors messages and warnings from SCCS commands.
Saturday, April 11, 2020
Operating systems video tutorial
Video Lectures of operating system are going live on YouTube everyday chapter wise. Please visit and get benefited.
Playlist link
https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLEAdcViuxDVJX406TP1Vc6gMME3JRLPCg
My Channel link
https://www.youtube.com/user/amitesh02
https://www.youtube.com/c/amiteshkumarsaha
Saturday, March 28, 2020
AMPLIFIER & REPEATER
An amplifier is an electronic device that increases the voltage, current, or power of a signal. Amplifiers are used in wireless communications and broadcasting, and in audio equipment of all kinds. They can be categorized as either weak-signal amplifiers or power amplifiers.
REPEATER
In digital communication systems, a repeater is a device that receives a digital signal on an electromagnetic or optical transmission medium and regenerates the signal along the next leg of the mediu
Video Tutorial
Video Lectures are going live on YouTube everyday chapter wise. Please visit and get benefited.
My Channel link
https://www.youtube.com/user/amitesh02
https://www.youtube.com/c/amiteshkumarsaha
Playlists are available now for
- Computer Graphics
- OSI Model
- Computer organization (IBM PC)
Everyday new videos will uploaded in different playlists.
Friday, February 28, 2020
MODEM
What is a modem?
The Importance of a Modem
Back in the old days, when landline phones were the primary tool to communicate over long distances, modems came in pretty handy to gain Internet connectivity using telephone lines. In fact, without modems, it would have been impossible for most users to connect to the Internet. While computer technology is purely digital, i.e., it relies on numbers to transmit and receive information, telephone technology, even to this day, is partly analog, meaning that it uses continuously varying electrical signals to transmit information.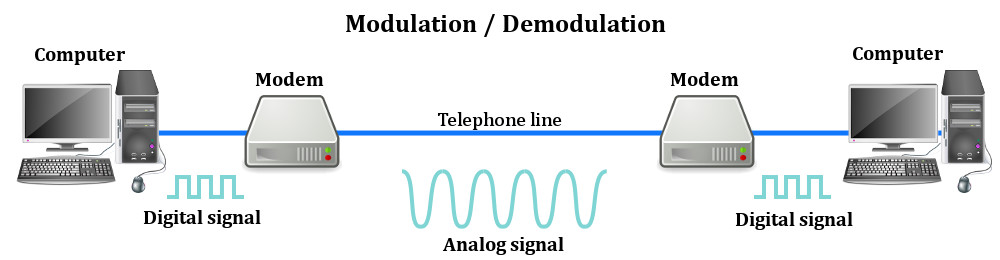
Wednesday, February 26, 2020
ETHERNET
- the physical media access control (MAC) addresses of both the sender and receiver;
- VLAN tagging and quality of service information;
- Error correction information to detect transmission problems.
Advantages of using wired Ethernet network
• It is very reliable.• Ethernet network makes use of firewalls for the security of the data.
• Data is transmitted and received at very high speed.
• It is very easy to use the wired network.
Disadvantages of using wired Ethernet network
• The wired Ethernet network is used only for short distances.• The mobility is limited.
• Its maintenance is difficult.
• Ethernet cables, hubs, switches, routers increase the cost of installation.
Types of Ethernet network
The maximum data rate of the original Ethernet technology is 10 megabits per second (Mbps), but a second generation fast ethernet carries 100 Mbps, and the latest version called gigabit ethernet works at 1000 Mbps. Ethernet network can be classified into 3 types:Fast Ethernet
This type of Ethernet can transfer data at a rate of 100 Mbps. Fast Ethernet makes use of twisted pair cable or fiber optic cable for communication.There are three types of fast Ethernet, which are as follows:
• 100BASE-TX
• 100BASE-FX
• 100BASE-T4
Gigabit Ethernet
This type of Ethernet network can transfer data at a rate of 1000 Mbps. Gigabit Ethernet also makes use of twisted pair cable or fiber optic cable. 48 bits used for addressing in Gigabit Ethernet. Nowadays gigabit Ethernet is very popular. The latest Gigabit Ethernet is a 10 Gigabit Ethernet, which can transfer data at a rate of 10 Gbps. Gigabit Ethernet was developed so that it can meet the needs of the user like faster communication network, faster transfer of data etc.Collision and Broadcast Domain
A collision domain is a network segment connected by a shared medium or through repeaters where simultaneous data transmissions collide with one another. The collision domain applies particularly in wireless networks, but also affected early versions of Ethernet. A network collision occurs when more than one device attempts to send a packet on a network segment at the same time. Members of a collision domain may be involved in collisions with one another. Devices outside the collision domain do not have collisions with those inside.


