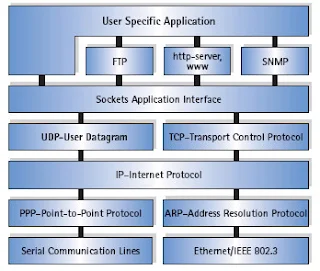
The Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) is a multiservice cellular network. It provides not only voice service, but a good set of data services as well. This chapter describes the data services offered by a GSM network. It describes the data services before the advent of GPRS and EDGE.
The GSM data services can be categorized in terms of traffic, signaling, and broadcast channel data services. The GSM standard specifies data services on the traffic channel (TCH), which can be utilized by data applications such as fax and Internet service provider (ISP) connection. This is also referred to as circuit switched (CS) data service. The data service on a signaling channel is known as the point-to-point short message service (SMS). Using SMS, a subscriber sends or receives a short string of text (maximum 126 characters) using a signaling channel. There is another type of SMS service called SMS broadcast, which is the only broadcast channel data service. This service transports data on a specially defined broadcast channel to all the subscribers in a cell. The broadcast data applications, such as traffic reports and weather alerts, were anticipated to use this service, but it didn't get much attention in deployment from cellular service providers.