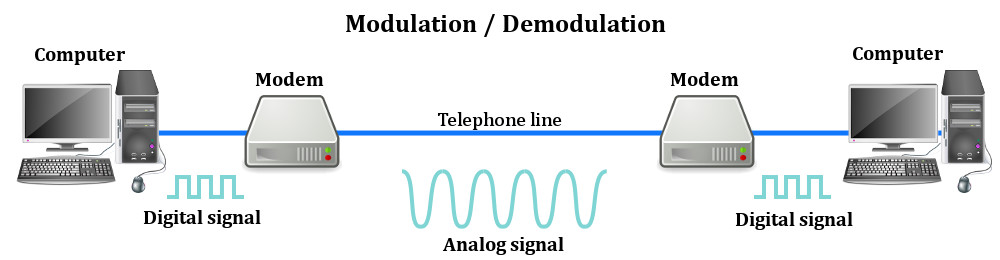
Modem is short for MOdulator
DEModulator. It’s an electronic device used to access the Internet that
modulates carrier waves to encode information to be transmitted and also
demodulates incoming carrier waves to decode the information they
carry.
What is a modem?
A
modem is a very important piece of network hardware that allows a
computer to send and receive data through a telephone line or cable
connection. In simple words, it’s the device that connects a computer to
the Internet using telecommunication network.
The Importance of a Modem
Back in the old days, when landline phones were the primary tool to communicate over long distances, modems came in pretty handy to gain Internet connectivity using telephone lines. In fact, without modems, it would have been impossible for most users to connect to the Internet. While computer technology is purely digital, i.e., it relies on numbers to transmit and receive information, telephone technology, even to this day, is partly analog, meaning that it uses continuously varying electrical signals to transmit information.
Since your modem sends information
through a telephone line by modulating digital signals, it also needs to
have another kind of translator that helps it demodulate the analog
signals it receives via the telephone line.